Discover Ganj Namah, Bhai Nand Lal's poetic tribute in Persian honoring the Ten Sikh Gurus, reflecting profound devotion and spiritual brilliance.
Discover the multifaceted term 'Meli' in Sikhism, from a verb to a title for preachers, reflecting its rich historical and religious significance.
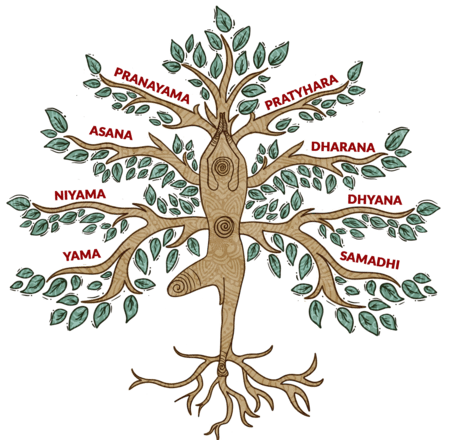
Unlock higher knowledge with Yoga. Dive into practices like Hatha, Mantra, and Rajyoga to achieve mental calm and spiritual insight.
GIANI SAMPRADAI is one of three major schools of Sikhs theologians and expositors of the Sikh scripture, the other two being the Udasis and the Nirmalas. Giani, the Punjabi form of Sanskrit jndni from the rootjnd (to know), originally meant a scholar of high learning. In Sikh tradition, a gidmis a learned man of pious character, competent to recite faultlessly, interpret and expound the Guru Granth Sahib and other Sikh religious texts. Sampraddi denotes a sectarian system or school of thought of accredited standing. It is claimed that the school of Gianis originated with Bhai Mani Singh (d. 1737) who had the privilege of receiving instruction from Guru Tegh Bahadur and Guru Gobind Singh.
Discover Parchi, a unique genre of Punjabi literature showcasing the spiritual tales of saints and prophets from the 17th century.
Explore the intriguing world of apocryphal Sikh compositions, unaccepted in the Guru Granth Sahib, exploring their origins and spiritual insights.
GOPI MAHITA, BHAI, accompanied by Bhai Tirath, Bhai Nattha, Bhai Bhau Mokal and Bhai Dhilli Mandal, once visited Guru Arjan. One of them, as says Bhai Mani Singh, Sikhdn d~i Bhagat Maid, said: "Lord, Prithi Mall and Mahadev [the Guru`s brothers] are also composing verses using the name of (Guru) Nanak as nom de plume which makes it difficult to know the genuine from the counterfeit." The Guru, addressing himself to Bhai Gurdas, spoke: "Today there are many Sikhs who know which are the true compositions of the Gurus, but tomorrow there may be none. The hymns of the Gurus should therefore be collected and compiled into a single volume.
Explore 'Parchian Seva Das', an 18th-century collection of sakhees from Sikh Gurus with insights into Sikh tenets and historical anecdotes.
Uncover the pivotal role of Guru Arjan Dev in Sikhism's evolution. His teachings, leadership, and contributions shaped Sikh tradition profoundly.
Explore Saundha Singh's Gurbansavau, a poetic chronology of the Sikh Gurus, blending history and literature in Hindi-Punjabi verse.